Harry Fletcher
Oct 20, 2024
Human DNA Discovered in Neanderthal Remains Dating Back Hundreds of Thousands of …
ZMG - Amaze Lab / VideoElephant
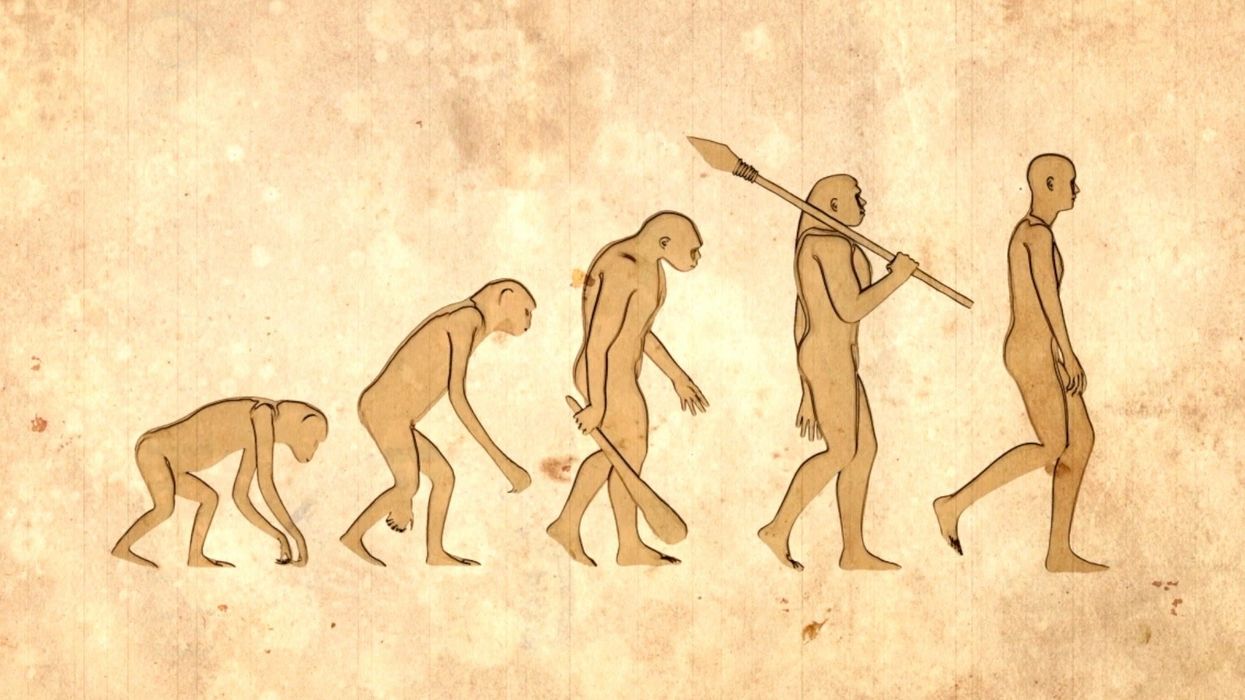
What’s the most enigmatic human ancestor, that we probably know the least about? There’s a good chance it’s the Red Deer Cave people.
Despite walking on Earth relatively recently – only around 14,000 years ago or so – they had more in common with human ancestors dating back far, far earlier.
The first time scientists ever focused on them properly came back in 1989, when remains were found in Yunnan in southern China. The site was also home to red deer fossils, hence the ancestors being dubbed ‘the Red Deer Cave people’.
They remained something of a mystery until studies into them stepped up in 2012.
Researchers at that time found that the remains more closely resembled long extinct human ancestors than modern day humans. Analysis also showed that they had flat faces with prominent brow ridges.
Darren Curnoe, who is an evolutionary biologist at the University of New South Wales, told National Geographic at the time [via IFL Science]: "We have discovered a new population of prehistoric humans whose skulls are an unusual mosaic of primitive features, like those seen in our ancestors hundreds of thousands of years ago.”
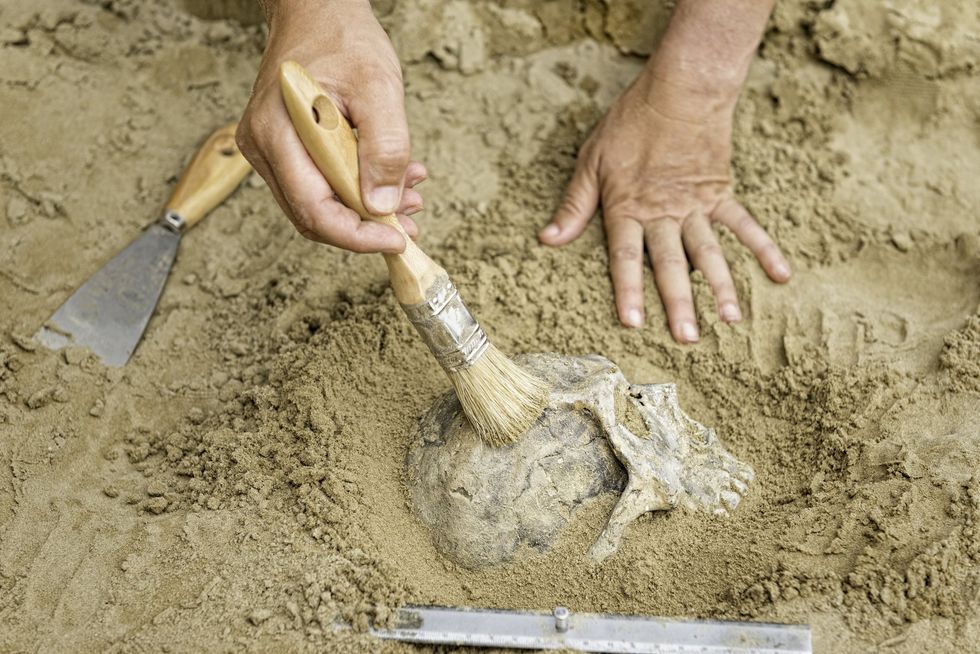

"In short, they're anatomically unique among all members of the human evolutionary tree," he added.
Then, further information arrived in 2015 when a femur bone was uncovered at the site.
The new find suggested that the species had more in common with far older human ancestors, experts were able to establish that the Red Deer Cave people weighed around 50 kilograms and had shared features with early Homo erectus, which went extinct around 1.5 million years ago – which is remarkable considering that the Red Deer Cave people only lived around 14,000 years ago.
Speaking in 2015, Professor Ji Xueping from the Yunnan Institute of Cultural Relics and Archaeology said in a statement: “Its young age suggests the possibility that primitive-looking humans could have survived until very late in our evolution, but we need to be careful as it is just one bone.”
It comes after previous research revealed that all life on Earth derives from a single ancestor name LUCA.
This acronym stands for the “Last Universal Common Ancestor,” which scientists believe was a tiny, and very basic, organism.
Sign up for our free Indy100 weekly newsletter
How to join the Indy100's free WhatsApp channel
Have your say in our news democracy. Click the upvote icon at the top of the page to help raise this article through the Indy100 rankings
Top 100
The Conversation (0)