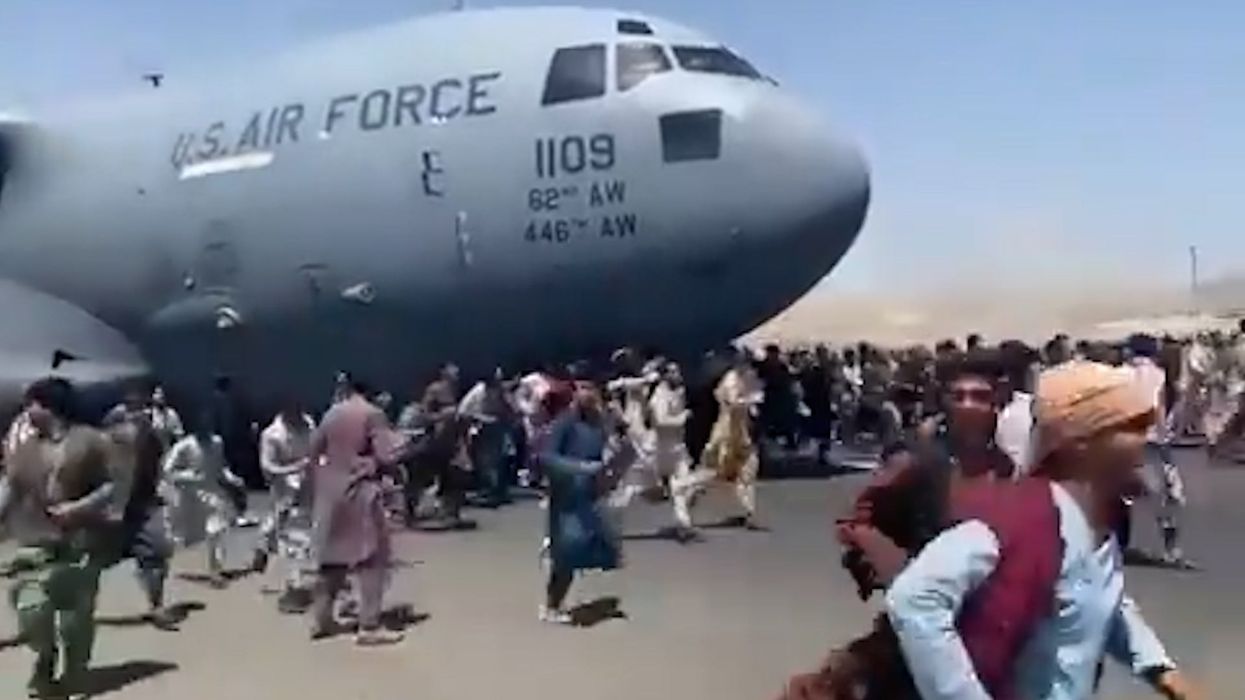
Yesterday, the Taliban seized control of Afghanistan’s capital city, Kabul, and announced it would be implementing a Taliban government in the country for the first time since 2001, when its regime was last ousted by Western troops.
President Ashraf Ghani fled the country “to avoid bloodshed” and said the Taliban had won the 20 year war in the region, in a statement. Meanwhile, thousands of people attempted to flee the country, fearing the strict ideology that the Taliban will likely implement in the country.
There has been conflict in the region for over 20 years with a US military presence in the country since 2001. This is what has happened in that time frame:
Origins
The Taliban, which means ‘students’ in the Pashto language, were formed after the collapse of the Soviet Union – which controlled the territory – in 1989. They were one of several factions fighting to gain command of the country in a civil war.
By 1996, they had gained control of several areas and imposed Sharia law on the country.
Start of the war
In 2001, US troops entered the country to oust the regime after they housed Osama bin-Laden and several other Al-Qaeda figures in the wake of the 9/11 attacks on the World Trade Center in New York, in which some 3,0000 people died.
At the time, President George Bush said: “These carefully targeted actions are designed to disrupt the use of Afghanistan as a terrorist base of operations, and to attack the military capability of the Taliban regime.”
Taliban forces have fought guerrilla wars with US and NATO forces since then and more than 120,000 Afghans have died. In 2011, the number of US troops in the country peaked at around 110,000.
De-escalation
Nato formally ended its combat mission in December 2014, but kept a 13,000-strong force there to help train Afghan forces and support counter-terrorism operations. However, that gave the Taliban momentum and they seized more territory.
The Taliban entered into talks with the US in 2018 and struck a peace deal in February 2020 which committed the US to withdraw its troops while preventing the Taliban from attacking US forces. But the Taliban just switched the focus of their attacks to Afghan security forces and civilians. Then, after US president Joe Biden committed to withdrawing the remainder of US troops this April, the insurgents renewed their attacks and have now taken over the country.
The Biden administration is now expected to make a statement in upcoming days while Parliament has been recalled in the UK and will sit on Wednesday to discuss actions.
More will doubtlessly follow in the days ahead.